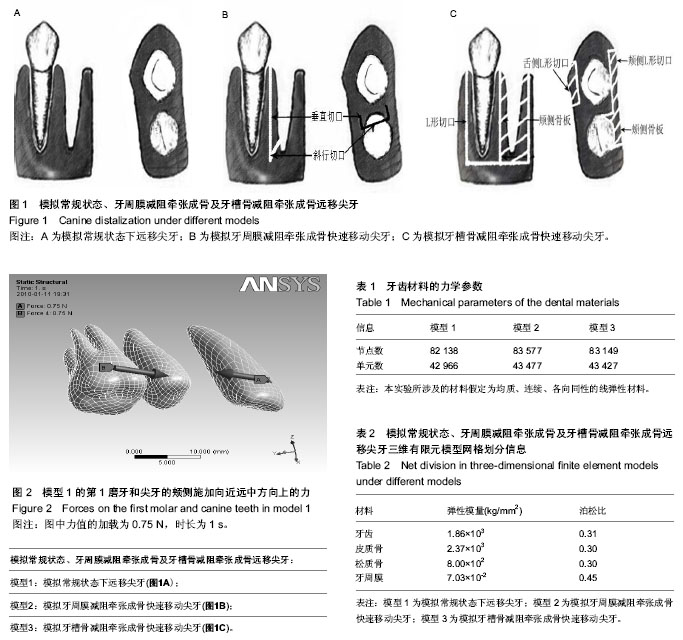
| [1] Hsler R, Schmid G, Ingervall B, et al. A clinical comparison of the rate of maxillary canine retraction into healed and recent extraction sites-a pilot study. Eur J Orthod. 1997;19(6): 711-719.[2] Liou EJ, Huang CS. Rapid canine retraction through distraction of the periodontal ligament. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998;114(4):372-82.[3] Allgayer S, Rosenbach G, Tavares CA,et al. Periodontal ligament distraction: esthetics and occlusal stability at the 2-year follow-up.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2013; 143:535-546.[4] 娄新田,房兵,沈国芳,等. 牵张成骨区牙移动动物模型的建立[J]. 上海口腔医学2011,20(1):21-25.[5] 陈曦,周洪,王静. 牙周膜牵张成骨正畸牙快速移动规律与牙根组织变化的光镜观察[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版, 2002, 23(5):496-498.[6] 陈曦,林珠,张晓东. 减阻牵张正畸牙移动过程中牙周组织超微结构的变化[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周学杂志, 2004,14(11): 615-617.[7] 陈曦,林珠,张晓东,等. 减阻牵张矫治法正畸牙快速移动牙周组织改建的研究[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2005;26(8), 685-687.[8] 陈曦,杜红梅,韩冰.牙周膜牵张成骨快速牙移动动物模型的建立[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2004,25(5):449-452.[9] 王爽,叶湘玉,周洪,等. 牙周膜牵张正畸过程中牙根吸收的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2003,38(3):202.[10] 王爽,叶湘玉,周洪,等. 犬牙周膜牵张成骨正畸牙移动中牵张侧的组织学变化[J]. 上海口腔医学,2004,13(4) :312-314.[11] 祁涛,卢嘉静,葛振林,等. 减阻牵张快速牙齿移动的组织学变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(50): 9370-9373.[12] Lv T, Kang N, Wang C,et al. Biologic response of rapid tooth movement with periodontal ligament distraction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136:401-411.[13] Kisnisci RS, Iseri H, Tuz HH, et al. Dentoalveolar distraction osteogenesis for rapid orthodontic canine retraction.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60:389-394.[14] Kurt G, Iseri H,Kisnisci R. Rapid tooth movement and orthodontic treatment usingdentoalveolar distraction (DAD). Long-term (5 years) follow-up of a Class II case. Angle Orthod. 2010;80:597-606.[15] Kharkar VR,Kotrashetti SM.Transport dentoalveolar distraction osteogenesis-assisted rapid orthodontic canine retraction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010:109:687-693.[16] Iseri H, Kisnisci R, Bzizi N,et al. Rapid canine retraction and orthodontic treatment with dentoalveolar distraction osteogenesis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2005;127: 533-541;quiz 625.[17] 赵广敏,陈奎孚,李岩峰. 正畸方丝弓与多曲方丝弓简单受力的有限元对比研究[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志,2009,26: 1126-1129.[18] Liang W, Rong Q, Lin J,et al. Torque control of the maxillary incisors in lingual and labial orthodontics: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135:316-322.[19] Yan X, He W, Lin, T,et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the craniomaxillary complex during maxillary protraction with bone anchorage vs conventional dental anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2013;143: 197-205.[20] da Silva BR, Moreira Neto JJ, da Silva FI Jr, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the maxillary central incisor in two different situations of traumatic impact. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2013;16: 158-164.[21] Fatalla AA, Song K, Du T, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis for overdenture attachments supported by teeth and/or mini dental implants. J Prosthodont 2012;21: 604-613.[22] Dalkiz M, Zor M, Aykul H, et al. The three-dimensional finite element analysis of fixed bridge restoration supported by the combination of teeth and osseointegrated implants. Implant Dent.2002;11:293-300.[23] Ammar HH, Ngan P, Crout RJ, et al. Three-dimensional modeling and finite element analysis in treatment planning for orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;139:e59-71.[24] Li P, Mao J,Peng Z.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the mechanical stress on root from orthodontic tooth movement by sliding mechanics.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2007;27:745-747.[25] Sukurica Y, Karaman A, Gurel, H.G. et al. Rapid canine distalization through segmental alveolar distraction osteogenesis. Angle Orthod 77, 226-36 (2007).[26] Sayin S, Bengi AO, Gurton AU, et al. Rapid canine distalization using distraction of the periodontal ligament: a preliminary clinical validation of the original technique. Angle Orthod. 2004;74:304-315.[27] Kumar KV, Umashankar K,Kumar DP. Evaluation of canine retraction through distraction of the periodontal ligament: a clinical study. J Contemp Dent Pract.2012;13:799-805.[28] Prabhat KC, Maheshwari S, Gupta ND,et al. Periodontal ligament distraction: A simplified approach for rapid canine retraction.J Indian Soc Periodontol.2012;16:123-125. [29] Wilmes B, Drescher D.Vertical periodontal ligament distraction--a new method for aligning ankylosed and displaced canines. J Orofac Orthop.2009;70:213-223.[30] Long H, Pyakurel U, Wang Y, et al. Interventions for accelerating orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2013;83:164-171.[31] 赵峰,高勃,刘震侠. Dieom标准和Mimics软件辅助建立下颌骨三维有限元模型[J]. 西南国防医药,2005,15(5):479-481.[32] Gross MD, Arbel G,Hershkovitz I.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the facial skeleton on simulated occlusal loading. J Oral Rehabil. 2001;28: 684-694.[33] Wagner A, Krach W, Schicho K, et al. A 3-dimensional finite-element analysis investigating the biomechanical behavior of the mandible and plate osteosynthesis in cases of fractures of the condylar process. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2002;94:678-686.[34] Katada H, Arakawa T, Ichimura K,et al. Stress distribution in mandible and temporomandibular joint by mandibular distraction: a 3-dimensional finite-element analysis. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2009;50:161-168.[35] 周学军,赵志河,赵美英.下颌骨三维有限元模型的边界约束设计[J].华西口腔医学杂志,1999,17(1):29-32.[36] 白石柱,李涤尘,赵铱民,等. 多层螺旋CT在建立上颌骨三维有限元模型中的应用[J].中国临床康复, 2006,10(41):90-92.[37] 赵玺,薛俊杰,米丛波. 减阻牵张成骨术快速移动尖牙的三维有限元分析[J].中华医学美学美容杂志, 2012,18(4):294-297.[38] 马文盛. 牵张成骨快速正畸牙齿移动的实验与应用研究[D]. 石家庄市:河北医科大学. 2009.[39] 傅民魁. 口腔正畸专科教程[M].北京:人民卫生出版社出版, 2007:124.[40] 徐芸译. 口腔正畸学-现代原理与技术[M]. 天津:天津科技翻译出版公司出版, 1996:175.[41] 刘燕,丁寅,张明,等. 犬牙槽骨牵张成骨快速移动牙齿的实验研究[J]. 口腔医学研究,2007,23,(2)151-153. |
.jpg)